AR and MR curves under Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition (or Imperfect Competition)
In both the situations of monopoly and monopolistic competition a firm can have an independent price policy. In these market situations a firm can sell more goods at lower prices and would be able to sell less amount of goods at higher prices. Because of this reason AR and MR curves of the firm would be downward sloping curve. Furthermore, the MR curve does not coincide with the AR curve and remains below it; since the sale of an extra unit force down the price at which extra units can be sold, the sale of an extra unit results in a net addition to revenue of a amount less than its own selling price. The shapes of the AR and MR curves in these market situations are illustrated in the following example and diagram.
Example
| Units of a Commodity | TR
(Rs.) |
AR
(Rs.) |
MR
(Rs.) |
|
| 1 | 80 | 80 | – | |
| 2 | 140 | 70 | 60 | |
| 3 | 180 | 60 | 40 | |
| 4 | 200 | 50 | 20 | |
| 5 | 210 | 420 | 10 |
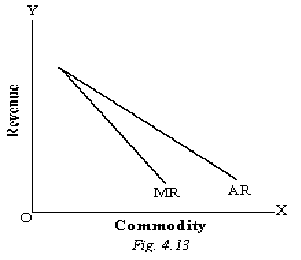

This was very helpful thankyou
thanks